Your body’s detoxification system is constantly hard at work eliminating dangerous toxins and invaders before they can harm you.
Six organs, in particular, have critical roles:
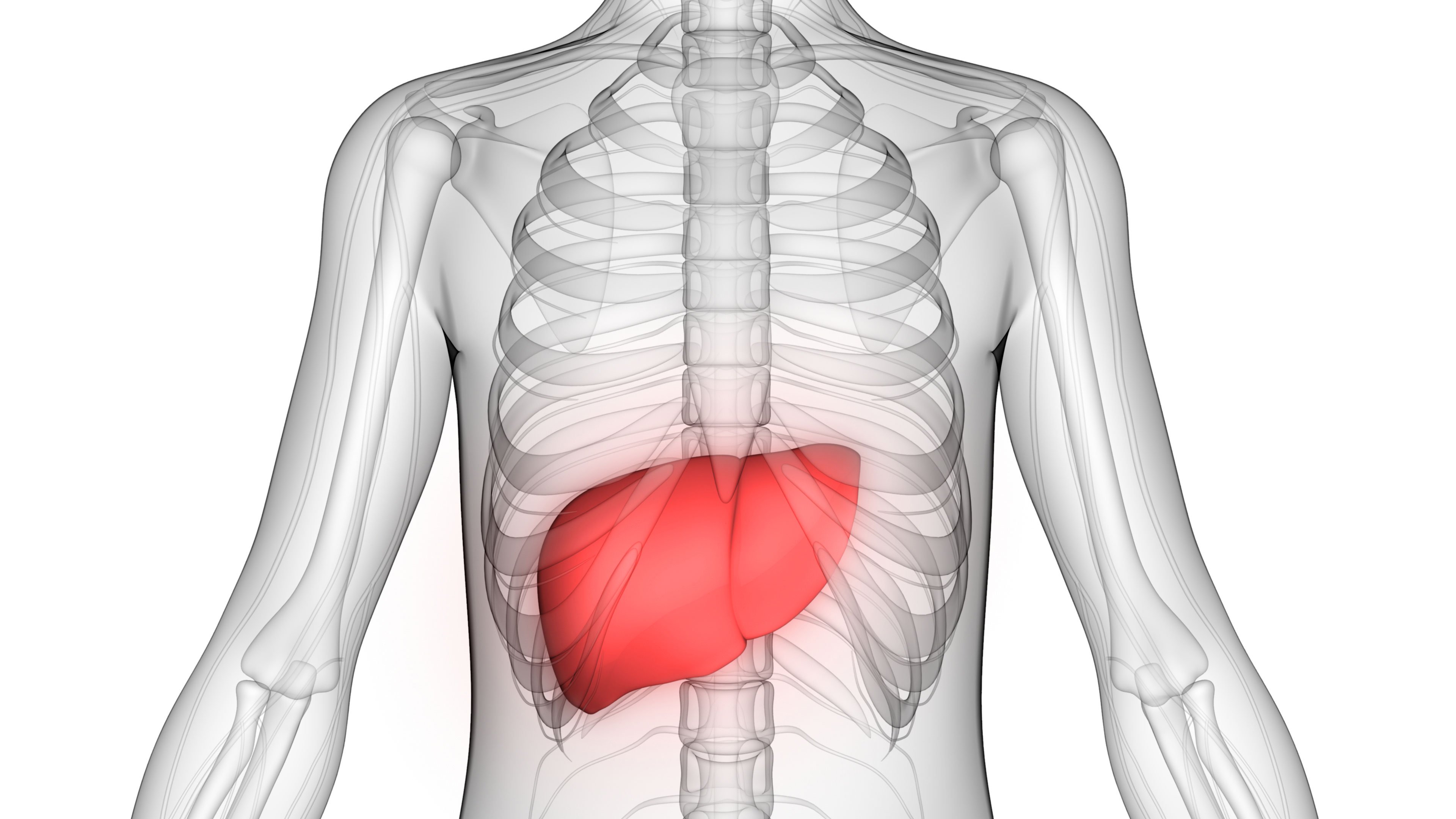
Your liver is your body’s most powerful weapon against toxins.
It performs some 500 functions. For example, it filters the blood and deactivates toxins. These toxins include food additives, medications, and excess hormones.
The liver also shuttles nutrients into your bloodstream. And it transforms the rest into waste material that exits your body via your kidneys or intestines.
You might think of your kidneys as the ultimate quality assurance team for your blood. They receive and filter your blood. And then, they excrete wastes from muscle metabolism and urea from protein breakdown.
They also eliminate excess fluid, bacteria, medications, and other chemicals through your urine.
Intestinal microflora breaks down nutrients, which are absorbed into your bloodstream. Toxins are routed to your small intestine and removed from your body through excrement.
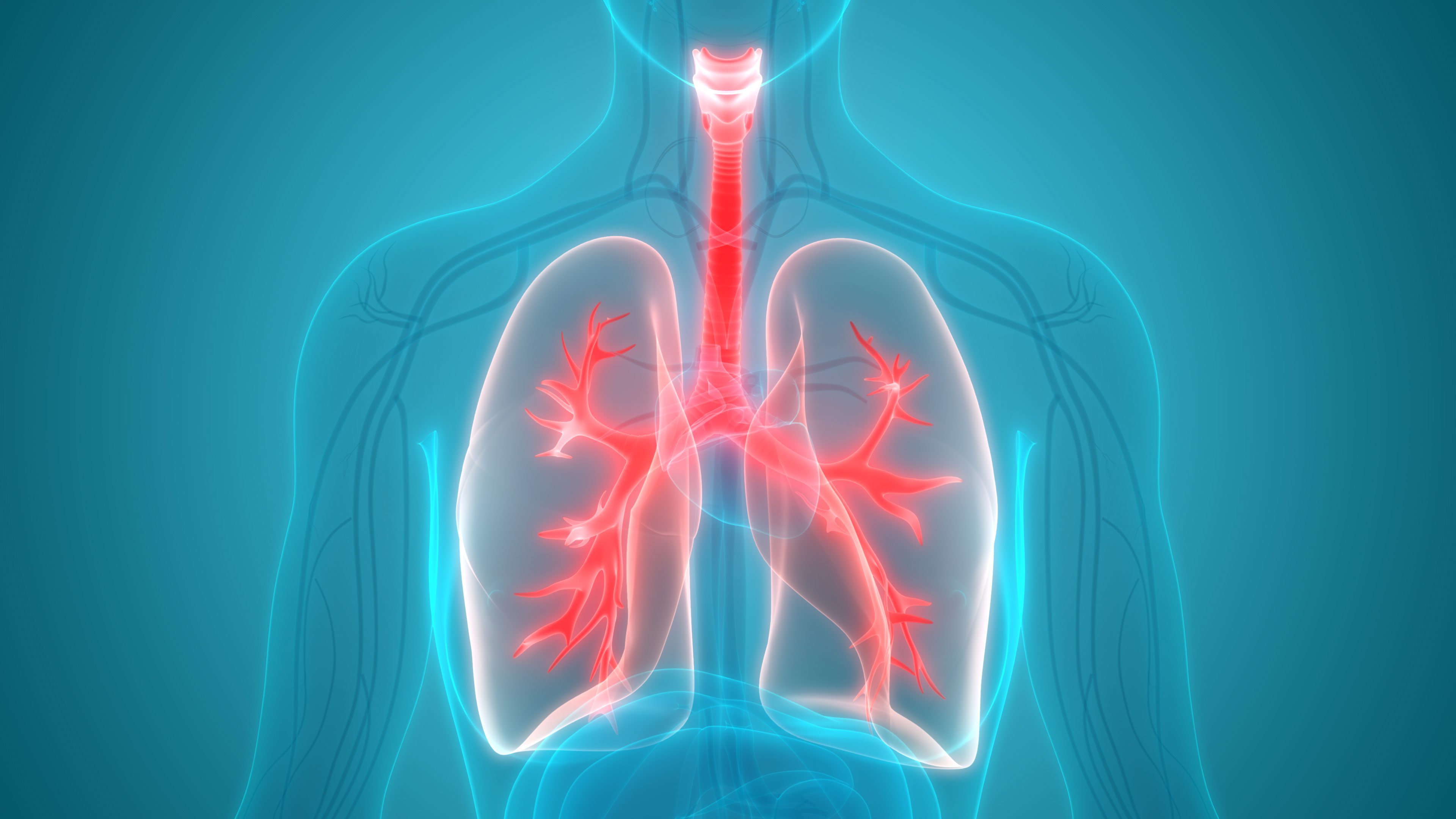 Your respiratory tract (lungs and bronchi) removes toxins mainly in the form of carbonic gas, as well as phlegm.
Your respiratory tract (lungs and bronchi) removes toxins mainly in the form of carbonic gas, as well as phlegm.
Your lungs are busy. They breathe in and out approximately 11,000 liters of air every day. And unlike the filters on vacuum cleaners and HVAC systems, you don’t need to replace them on a regular basis!
Research has found sweating assists in the elimination of BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals.
And while it can be porous (absorbing skin cream, for example), skin keeps out all sorts of bad things. It has the ability to block dangerous bacteria and even poisonous chemicals. In other words, skin is your body’s first line of defense against a broad array of toxins.
Its main purpose is to cleanse toxins and protect against invaders. Also, it carries waste away from your tissues and into your bloodstream where it can be processed and removed.
Pesticides, hormones, antibiotics, heavy metals, chemicals, and stress can all strain your natural detoxification systems. It’s like one person is mopping the floor while another is stomping around the kitchen in muddy boots.
And toxin exposure starts early. Before we’re even born, in fact. Testing of the umbilical cord blood of newborn babies has revealed an average of over 200 synthetic chemicals. And some of them have carcinogenic potential.
The effects many of these chemicals have on our bodies still aren’t fully understood. Yet evidence ties many of them to health problems.
And drinking water can be a source of toxins, too. Studies have found an array of chemicals in public water supplies including chlorine, lead, Chromium-6, and drug residues from antibiotics, antidepressants, hormones from birth control pills, and painkillers, among others.
Stress can also play a part. It diverts energy and other resources from the detox process.
The physiology of stress is rooted in the “fight or flight” response. The body interprets this as signaling a clear and present danger to our continued existence.
Detoxing when the body needs all its energy to escape from a predator would be like insisting on mopping the floor while a tornado bears down on your house.
But because most of our stressors are mental and emotional (traffic jams, financial worries, annoying emails), the body can under-prioritize detoxification even when it’s the most useful thing it could be doing.
Given the prevalence of toxins in our environment — and often also in our bodies — many people want to know what they can do to protect themselves.
Can you remove these harmful substances? Or will they stay with you for life?
The most common type of “detox” is a program that weans people off of alcohol and drugs. That makes sense. Because when someone is under the influence of these substances, they’re “intoxicated.” That is, they suffer from the effects of toxins in their bodies.
In natural health circles, detoxes are typically used to deal with environmental exposure to toxins, gastrointestinal disorders, and autoimmune diseases. They are also used for general cleansing and preventive medicine.
Practitioners who offer detoxes often claim that they can aid in weight loss, support digestion, and fight inflammation, allergies, bloating, and chronic fatigue.
Because “detox” has become such a massive health buzzword, the term is, unfortunately, used to sell a lot of products and services with no basis in science.
Some detox programs recommend using laxatives or diuretics, going into “starvation mode,” going overboard with unsustainable exercise routines, popping unproven (and expensive) supplements, drinking diet sodas sweetened with dangerous chemicals, or even going on a grapefruit diet. None of these approaches prove to help in the long run.
Do your research before you consider a new detox regimen or program. And remember — the best and safest way to detox is to eat real, healthy foods.
Unlike many of the popular “detox” programs and supplements out there, these foods help your body eliminate toxins. And they also provide many other positive health benefits, as well.
Here are 12 of the top detoxifying foods:
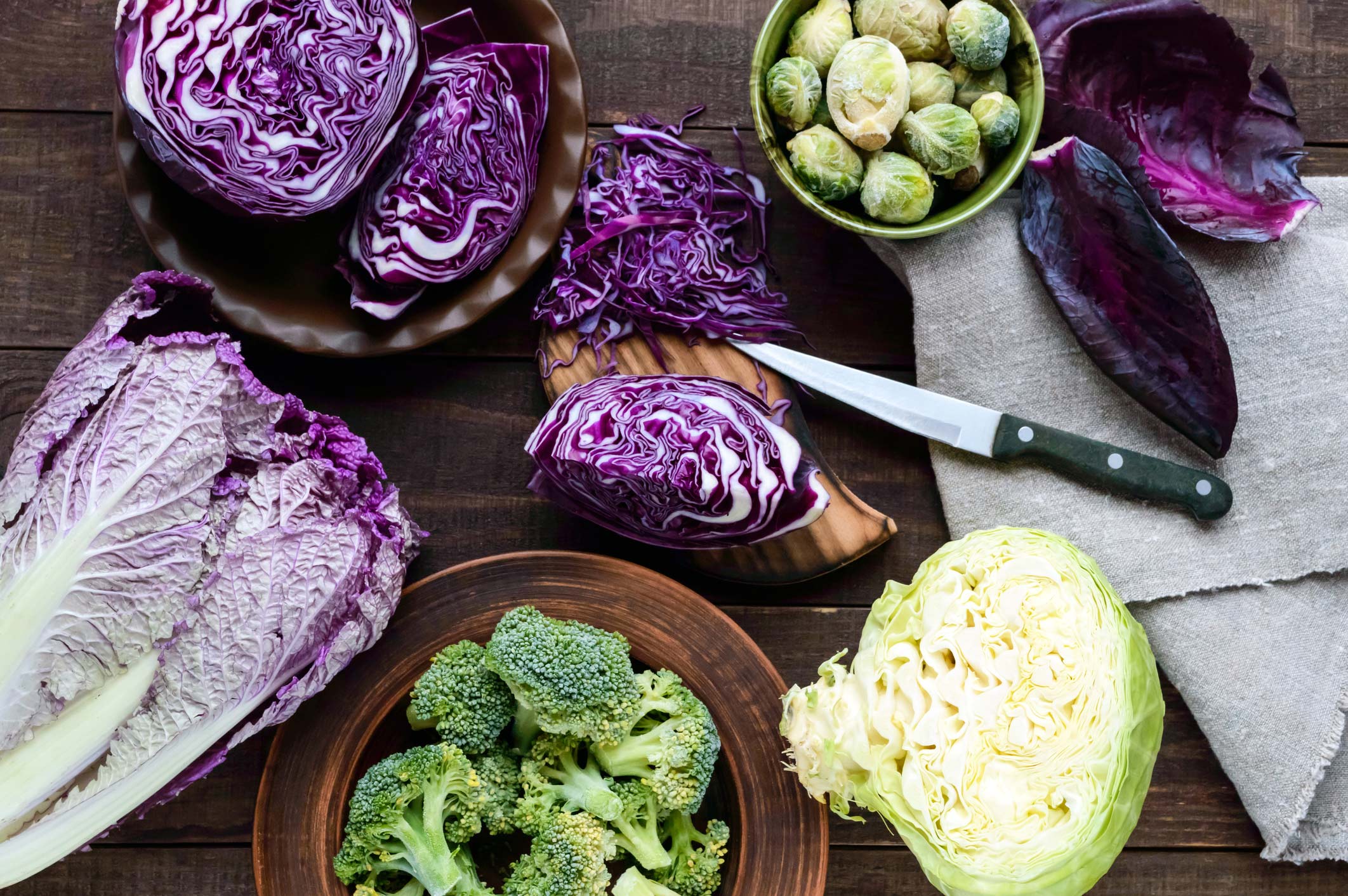

Cruciferous vegetables and leafy greens are on almost every list of
the world’s healthiest foods — and detoxifying foods are no exception.
This class of leafy veggies includes broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage,
Brussels sprouts, and bok choy, among others.
A 2015 study published in the journal Evidence Based Complementary Alternative Medicine reported that cruciferous veggies boost liver health through anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects. They’re also high in fiber, which encourages the excretion of toxins through bile and stool.
Spinach and dandelion greens — among other veggies on the list — are excellent sources of chlorophyll, which is considered the top detoxifying plant pigment.
And broccoli, in particular, has been linked to protection against air pollution. Broccoli sprouts also contain enzymes that protect against cancer-causing chemicals.
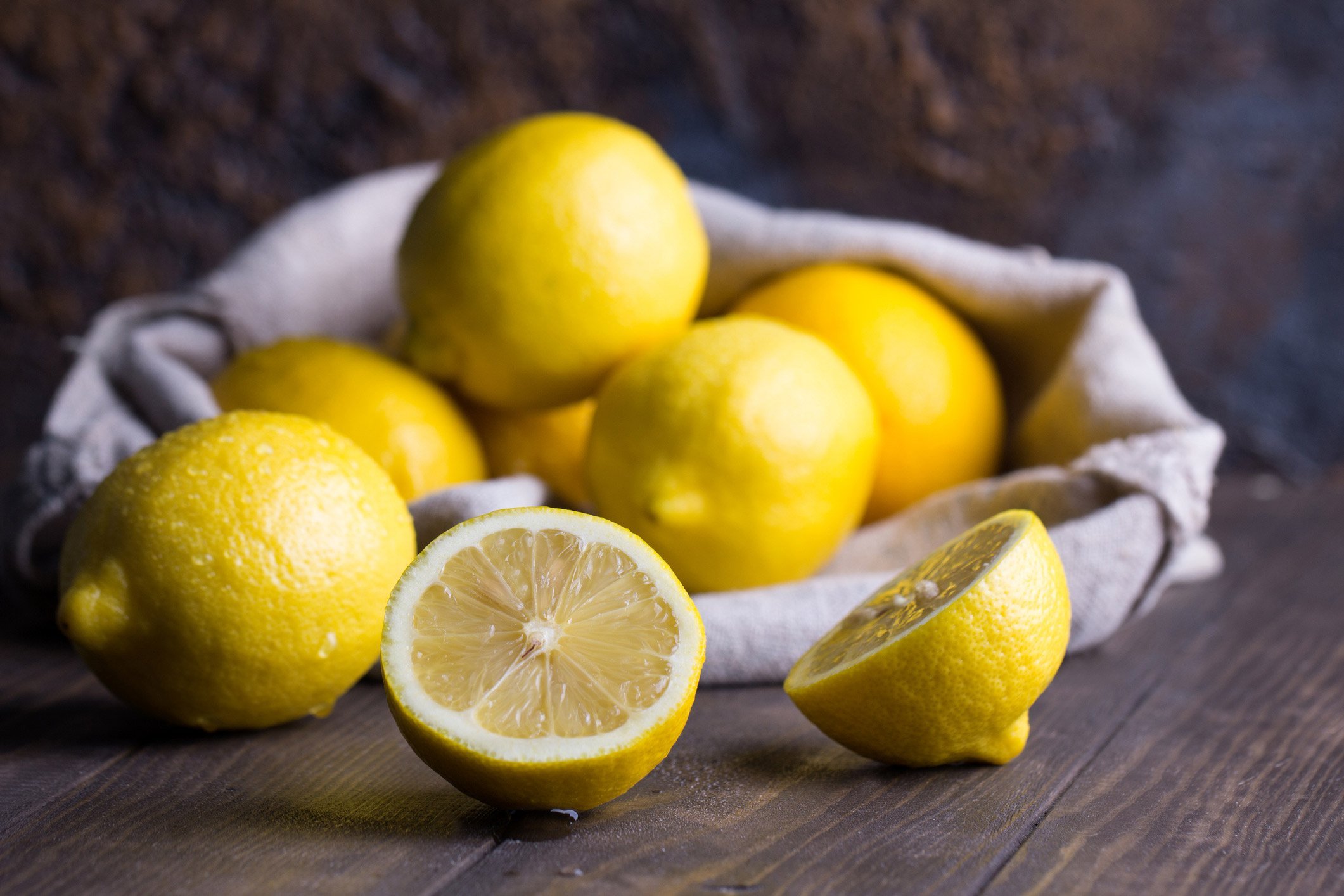

A 2014 study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food found that the citric acid in lemons can protect liver function and prevent oxidative (stress-related) damage.
Another 2014 study published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that daily lemon ingestion — combined with daily walking — helps regulate blood pressure.
Many people choose to consume lemon water to get their fill. All you need to do is squeeze fresh, organic lemon into a glass of water for an amped up version of H20. If you drink this a lot, you may want to drink it with a straw and rinse out your mouth with water right away.
(Be sure NOT to brush your teeth soon after drinking lemon water, or other acidic beverages. This could harm the enamel on your teeth.)
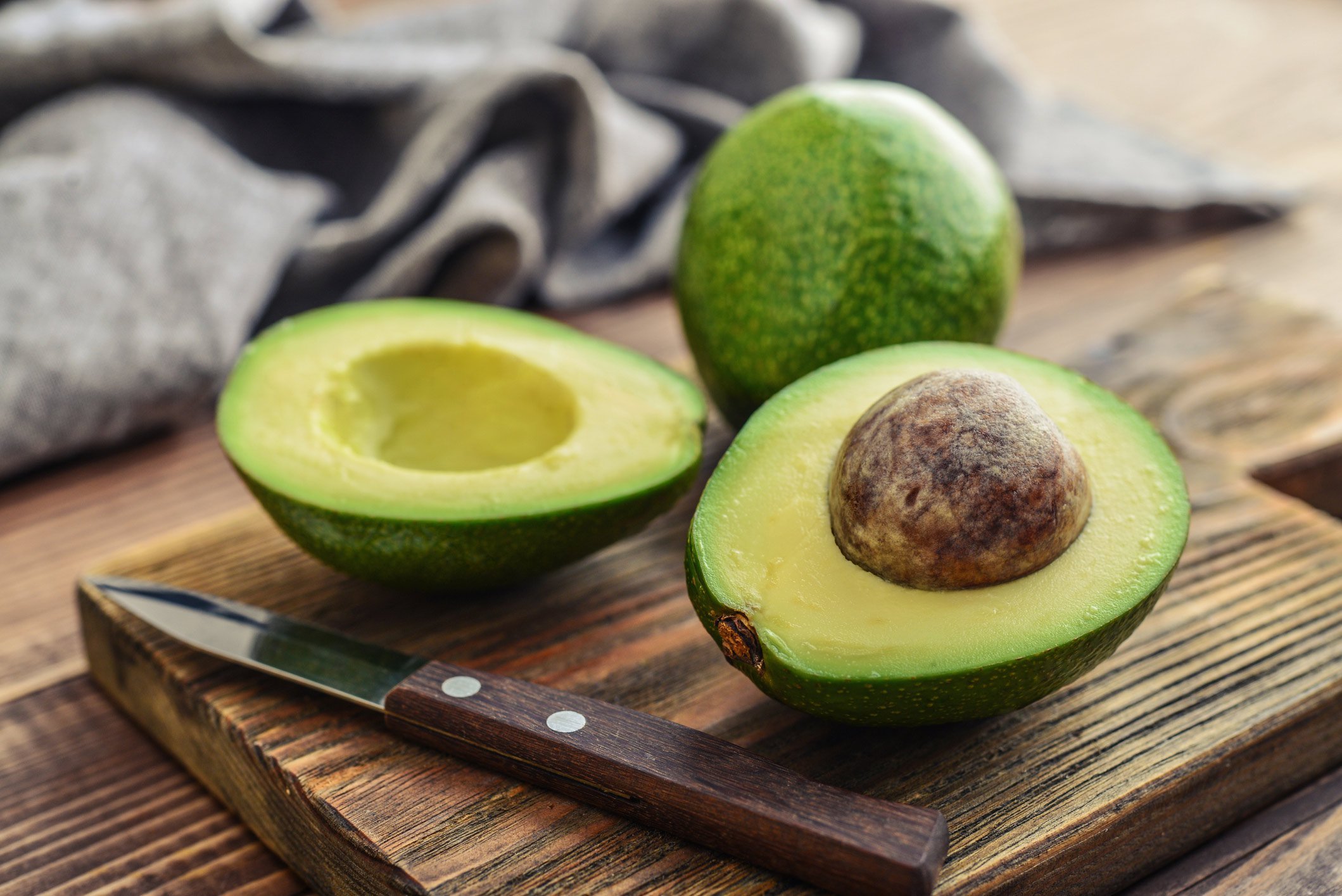

Dubbed “America’s new favorite fruit” because of its rise in popularity, avocados have a wealth of antioxidants and other nutrients.
A 2001 study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that the fatty acids in avocados help protect against damage caused by d-galactosamine, a powerful liver toxin.
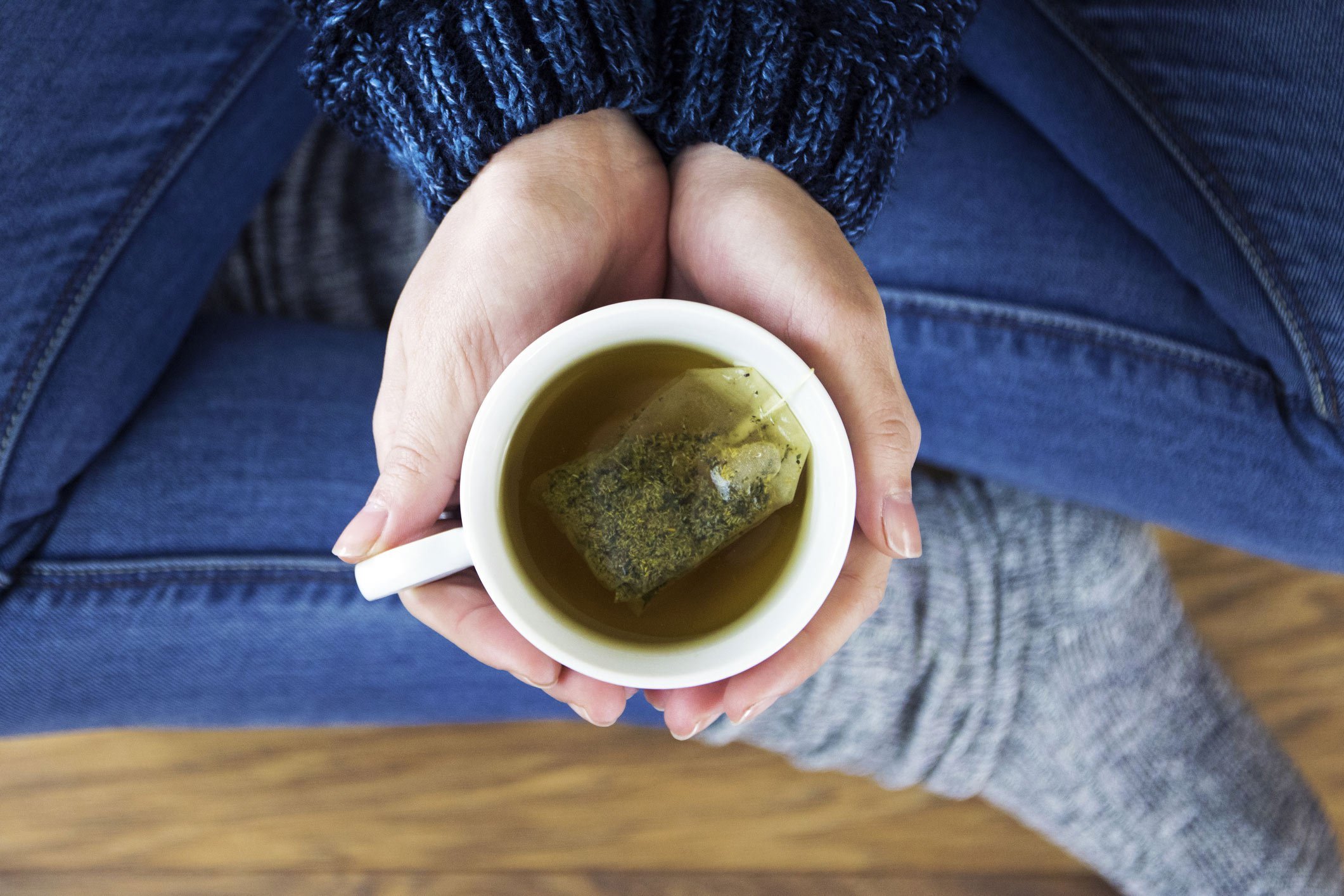 Green tea is universally considered a good-for-you beverage. And it’s been used as a medicinal aid for thousands of years.
Green tea is universally considered a good-for-you beverage. And it’s been used as a medicinal aid for thousands of years.
High in antioxidants, it helps keep your body in balance, protecting against free radicals that can cause aging and degenerative disease.
Green tea has also frequently been shown to have a protective effect against certain types of cancer.
A 2007 study published in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention found that a green tea concentrate boosted production of detoxification enzymes, which play a key role in cancer prevention.
Note: Pique Tea uses cold-brew crystallization (which eliminates heat and extracts the maximum antioxidant capacity from tea leaves) to create tea crystals — which deliver up to 12 times the antioxidants of regular tea.

These popular snacks are rich in the soluble fiber pectin. Pectin helps purge toxins from the bloodstream and lower LDL cholesterol.
A 2006 study published in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that pectin can aid in the excretion of toxins, such as mercury and lead.
 A 2014 research review on the studies about garlic published in the Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine found that this spicy veggie has a whole host of health benefits.
A 2014 research review on the studies about garlic published in the Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine found that this spicy veggie has a whole host of health benefits.
Researchers found that garlic can inhibit the activation of carcinogens, enhance detoxification, and even protect DNA.

With many positive effects for everything from mood to heart function, some consider this bright green alga to be a wonder food.
Chlorella has been shown to help with depression and anxiety, reduce excess weight, and lower LDL cholesterol. It also helps reduce liver inflammation.
Four grams or more (about two teaspoons) per day for at least eight weeks is the recommended amount to kickstart the benefits. If you like, you can stir it into your morning juice or add it to a smoothie!

Also known as “Indian saffron,” this gorgeous yellow spice has been used medicinally for nearly 4,000 years.
In 2011, the editors of Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects reviewed the evidence on this ancient spice. They found it to have “antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antioxidant, antiseptic, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, radioprotective, and digestive activities.”
The primary active ingredient in turmeric is curcumin, which gives it its bright yellow color. However, if you just eat turmeric straight, you may not absorb much. I love mixing fresh and dried turmeric into all sorts of foods. And I always try to include black pepper because studies show that piperine (found in black pepper) helps to increase curcumin absorption substantially.
Note: PuraTHRIVE has developed a curcumin supplement that uses a cutting-edge micelle liposomal delivery mechanism, which has been found to increase bioavailability by up to 185 times.

These bright-red veggies contain high levels of antioxidants and other health-promoting properties.
But beets are also a detox tool. A 2015 study published in the journal Nutrients found that beet juice can amplify specific enzymes that support the liver and aid in detoxification.

Besides being delicious, blueberries are nutrient-dense and are an abundant source of antioxidants.
They’ve been shown to lower blood pressure, boost vascular health, fight cancer, protect lungs, and prevent Alzheimer’s, among other effects.
As far as fighting toxins, a 2011 study published in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism found that the berries enhanced the activity of the body’s natural killer cells, which fight against cancer cells.
 Some plants can bind to heavy metals and help your body excrete them. Those plants are known as “chelators” and this flavorful herb is one of them!
Some plants can bind to heavy metals and help your body excrete them. Those plants are known as “chelators” and this flavorful herb is one of them!
A 2013 study published in Scientific World Journal found that cilantro can enhance mercury excretion and decrease lead absorption.

Rich in phytochemicals — the healthy compounds found in plants — many people use ginger as a gastrointestinal aid.
Since the intestines perform so much detoxification work, ginger can help boost your body’s ability to process food and eliminate waste.
A 2013 research review published in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine found that ginger protects against oxidative stress, has anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects, and offers a wealth of antioxidants.
Source Click here
Six organs, in particular, have critical roles:
The Liver

It performs some 500 functions. For example, it filters the blood and deactivates toxins. These toxins include food additives, medications, and excess hormones.
The liver also shuttles nutrients into your bloodstream. And it transforms the rest into waste material that exits your body via your kidneys or intestines.
The Kidneys
Kidneys perform several functions, including regulating fluid and electrolyte balance in your body. They also help to control your blood pressure and deal with hormone secretion.You might think of your kidneys as the ultimate quality assurance team for your blood. They receive and filter your blood. And then, they excrete wastes from muscle metabolism and urea from protein breakdown.
They also eliminate excess fluid, bacteria, medications, and other chemicals through your urine.
The Gastrointestinal System
From your mouth to your colon, your intestinal tract both digests foods and helps to eliminate toxins.Intestinal microflora breaks down nutrients, which are absorbed into your bloodstream. Toxins are routed to your small intestine and removed from your body through excrement.
The Respiratory Tract

iStock.com/magicmine
Your lungs are busy. They breathe in and out approximately 11,000 liters of air every day. And unlike the filters on vacuum cleaners and HVAC systems, you don’t need to replace them on a regular basis!
The Skin
Skin is, technically, an organ. It plays an important role in the elimination of toxins.Research has found sweating assists in the elimination of BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals.
And while it can be porous (absorbing skin cream, for example), skin keeps out all sorts of bad things. It has the ability to block dangerous bacteria and even poisonous chemicals. In other words, skin is your body’s first line of defense against a broad array of toxins.
The Lymphatic System
Your lymphatic system includes fluid-filled nodes, vessels, glands, and organs.Its main purpose is to cleanse toxins and protect against invaders. Also, it carries waste away from your tissues and into your bloodstream where it can be processed and removed.
Why We’re Overloaded with Toxins
Your body’s detoxification system is powerful. But in our modern age, it’s also likely under considerable pressure.Pesticides, hormones, antibiotics, heavy metals, chemicals, and stress can all strain your natural detoxification systems. It’s like one person is mopping the floor while another is stomping around the kitchen in muddy boots.
And toxin exposure starts early. Before we’re even born, in fact. Testing of the umbilical cord blood of newborn babies has revealed an average of over 200 synthetic chemicals. And some of them have carcinogenic potential.
The effects many of these chemicals have on our bodies still aren’t fully understood. Yet evidence ties many of them to health problems.
And drinking water can be a source of toxins, too. Studies have found an array of chemicals in public water supplies including chlorine, lead, Chromium-6, and drug residues from antibiotics, antidepressants, hormones from birth control pills, and painkillers, among others.
Stress can also play a part. It diverts energy and other resources from the detox process.
The physiology of stress is rooted in the “fight or flight” response. The body interprets this as signaling a clear and present danger to our continued existence.
Detoxing when the body needs all its energy to escape from a predator would be like insisting on mopping the floor while a tornado bears down on your house.
But because most of our stressors are mental and emotional (traffic jams, financial worries, annoying emails), the body can under-prioritize detoxification even when it’s the most useful thing it could be doing.
Given the prevalence of toxins in our environment — and often also in our bodies — many people want to know what they can do to protect themselves.
Can you remove these harmful substances? Or will they stay with you for life?
Does “Detoxing” Help?
The term “detox” has many different uses.The most common type of “detox” is a program that weans people off of alcohol and drugs. That makes sense. Because when someone is under the influence of these substances, they’re “intoxicated.” That is, they suffer from the effects of toxins in their bodies.
In natural health circles, detoxes are typically used to deal with environmental exposure to toxins, gastrointestinal disorders, and autoimmune diseases. They are also used for general cleansing and preventive medicine.
Practitioners who offer detoxes often claim that they can aid in weight loss, support digestion, and fight inflammation, allergies, bloating, and chronic fatigue.
Because “detox” has become such a massive health buzzword, the term is, unfortunately, used to sell a lot of products and services with no basis in science.
Some detox programs recommend using laxatives or diuretics, going into “starvation mode,” going overboard with unsustainable exercise routines, popping unproven (and expensive) supplements, drinking diet sodas sweetened with dangerous chemicals, or even going on a grapefruit diet. None of these approaches prove to help in the long run.
Do your research before you consider a new detox regimen or program. And remember — the best and safest way to detox is to eat real, healthy foods.
How Detoxifying Foods Can Boost Your Detox Ability
Research shows there are specific foods that can help your body boost its detox power.Unlike many of the popular “detox” programs and supplements out there, these foods help your body eliminate toxins. And they also provide many other positive health benefits, as well.
Here are 12 of the top detoxifying foods:
1) Cruciferous Vegetables and Leafy Greens

A 2015 study published in the journal Evidence Based Complementary Alternative Medicine reported that cruciferous veggies boost liver health through anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral effects. They’re also high in fiber, which encourages the excretion of toxins through bile and stool.
Spinach and dandelion greens — among other veggies on the list — are excellent sources of chlorophyll, which is considered the top detoxifying plant pigment.
And broccoli, in particular, has been linked to protection against air pollution. Broccoli sprouts also contain enzymes that protect against cancer-causing chemicals.
2) Lemon

Another 2014 study published in the Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism found that daily lemon ingestion — combined with daily walking — helps regulate blood pressure.
Many people choose to consume lemon water to get their fill. All you need to do is squeeze fresh, organic lemon into a glass of water for an amped up version of H20. If you drink this a lot, you may want to drink it with a straw and rinse out your mouth with water right away.
(Be sure NOT to brush your teeth soon after drinking lemon water, or other acidic beverages. This could harm the enamel on your teeth.)
3) Avocado

A 2001 study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry found that the fatty acids in avocados help protect against damage caused by d-galactosamine, a powerful liver toxin.
4) Green Tea

iStock.com/PredragImages
High in antioxidants, it helps keep your body in balance, protecting against free radicals that can cause aging and degenerative disease.
Green tea has also frequently been shown to have a protective effect against certain types of cancer.
A 2007 study published in the journal Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention found that a green tea concentrate boosted production of detoxification enzymes, which play a key role in cancer prevention.
Note: Pique Tea uses cold-brew crystallization (which eliminates heat and extracts the maximum antioxidant capacity from tea leaves) to create tea crystals — which deliver up to 12 times the antioxidants of regular tea.
5) Apples

A 2006 study published in the journal Phytotherapy Research found that pectin can aid in the excretion of toxins, such as mercury and lead.
6) Garlic

iStock.com/Amarita
Researchers found that garlic can inhibit the activation of carcinogens, enhance detoxification, and even protect DNA.
7) Chlorella

Chlorella has been shown to help with depression and anxiety, reduce excess weight, and lower LDL cholesterol. It also helps reduce liver inflammation.
Four grams or more (about two teaspoons) per day for at least eight weeks is the recommended amount to kickstart the benefits. If you like, you can stir it into your morning juice or add it to a smoothie!
8) Turmeric

In 2011, the editors of Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects reviewed the evidence on this ancient spice. They found it to have “antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antioxidant, antiseptic, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, nephroprotective, radioprotective, and digestive activities.”
The primary active ingredient in turmeric is curcumin, which gives it its bright yellow color. However, if you just eat turmeric straight, you may not absorb much. I love mixing fresh and dried turmeric into all sorts of foods. And I always try to include black pepper because studies show that piperine (found in black pepper) helps to increase curcumin absorption substantially.
Note: PuraTHRIVE has developed a curcumin supplement that uses a cutting-edge micelle liposomal delivery mechanism, which has been found to increase bioavailability by up to 185 times.
9) Beets

But beets are also a detox tool. A 2015 study published in the journal Nutrients found that beet juice can amplify specific enzymes that support the liver and aid in detoxification.
10) Blueberries

They’ve been shown to lower blood pressure, boost vascular health, fight cancer, protect lungs, and prevent Alzheimer’s, among other effects.
As far as fighting toxins, a 2011 study published in the journal Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism found that the berries enhanced the activity of the body’s natural killer cells, which fight against cancer cells.
11) Cilantro

iStock.com/MmeEmiljpg
A 2013 study published in Scientific World Journal found that cilantro can enhance mercury excretion and decrease lead absorption.
12) Ginger

Since the intestines perform so much detoxification work, ginger can help boost your body’s ability to process food and eliminate waste.
A 2013 research review published in the International Journal of Preventive Medicine found that ginger protects against oxidative stress, has anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects, and offers a wealth of antioxidants.
Source Click here
Comments
Post a Comment